Identify the electrophile for the Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene. The mechanism for this reaction begins with the generation of a methyl carbocation from methylbromide.

Solved Identify The Electrophile In A Friedel Crafts Chegg Com
The purpose of this experiment is to make a dialkylated product using an unknown tertiary alcohol and 14-dimethoxybenzene via Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
. Which one of the following reactions is most likely to give a polysubstituted product. 1 Initially a complex is formed due to coordination of alkyl halide to the Lewis acid. One example is the addition of a methyl group to a benzene ring.
However benzene is not a very good nucleophile and cannot react directly with the alkyl halide. An alkyl group can be added to a benzene molecule by an electrophile aromatic substitution reaction called the FriedelCrafts alkylation reaction. EAS Friedel Crafts Alkylation Reaction Electrophile Mechanism H This is a very useful reaction because you can make carbon-carbon bonds to aromatic compounds.
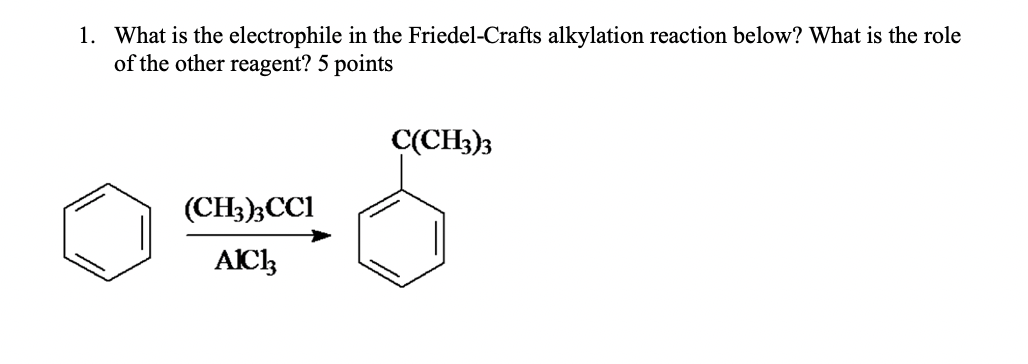
The one that will react with the benzene ring O aluminum. In the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction the benzene ring acts as a nucleophile and an alkyl halide acts as an electrophile. Identify the electrophile in a Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
The hydrogen is removed by the AlCl 4-ion which was formed at the same time as the CH 3 electrophile. MECHANISM FOR THE FRIEDEL-CRAFTS ALKYLATION OF BENZENE. Careful attention should be paid to side reactions that often occur when the carbocation electrophile can rearrange to a more stable one.
Solution for Question 12 Identify the electrophile in a Friedel-Crafts alkylation remember. The alkyl halide reacts with the Lewis acid to form a a more electrophilic C a carbocation. If you are going to replace a hydrogen atom in a benzene ring.
Similar to the FriedelCrafts acylation the electron-donating groups facilitate the alkylation whereas the electron-withdrawing groups impede the alkylation. Name the electrophiles which participate in the following reactions. To overcome this a strong Lewis acid is used to help catalyse the reaction.
This complex may act as the electrophilic reagent or it may dissociate to give a free carbocation which can act as electrophile. An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction occurs during a friedel-crafts alkylation reaction. In addition an acidic catalyst either a Brønsted.
In a Clemmensen reduction an aryl ketone is reduced to _____. The nucleophile of this reaction is the 14-dimethoxybenzene which attacks the electrophile and creates a resonance stabilized. MECHANISM OF FRIEDEL CRAFTS ALKYLATION.
A carbocation is the electrophile of this reaction and is generated by protonating the tertiary alcohol. Aluminium trichloride AlCl 3 is often used as a catalyst in Friedel-Crafts reactions since it acts as a Lewis acid and coordinates with the halogens generating an electrophile in the process. Loss of the halide to the Lewis acid forms the electrophilic alkyl carbocation.
A Lewis acid is a molecule with an empty orbital that can accept an. Nitration chlorination Friedel-Crafts alkylation Friedel-Crafts acylation and sulphonation. The FriedelCraft alkylation is a special class of electrophilic aromatic substitution in which the electrophile is a carbocation.
If you want the Friedel-Crafts alkylation mechanism explained to you in detail there is a link at the bottom of the page. The reaction involves the alkylation of a the aromatic ring when an alkyl halide is reacted with the compound in the presence of aluminum chloride. Explaining the mechanism for the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene - an electrophilic substitution reaction between benzene and a chloroalkane.
Friedel Crafts Alkylation Part -02 and Friedel Crafts Acylation Reaction OF Benzene. The formation of the electrophile. In that reaction an electrophile is formed from a reaction between alkyl halide and lewis acid where the lewis acid removes the halide in the alkyl halide thereby creating a carbocation which acts as an electrophile.
The aluminium chloride catalyst is. 2 The next step involves the addition of the complex or the carbocation to the aromatic system to give a σ. Friedel-Crafts Alkylation refers to the replacement of an aromatic proton with an alkyl group.
Friedel-Crafts alkylation is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction underwent by aromatic compounds. Electrophiles that are primary carbocations are quite unstable and very reactive.

Eas Reactions 3 Friedel Crafts Acylation And Friedel Crafts Alkylation Chemistry Organic Chem Organic Chemistry

Solved 1 What Is The Electrophile In The Friedel Crafts Chegg Com

Solved Testbank Question 023 Identify The Electrophile In A Chegg Com

Eas Reactions 3 Friedel Crafts Acylation And Friedel Crafts Alkylation Chemistry Organic Chemistry Reactions
0 Comments